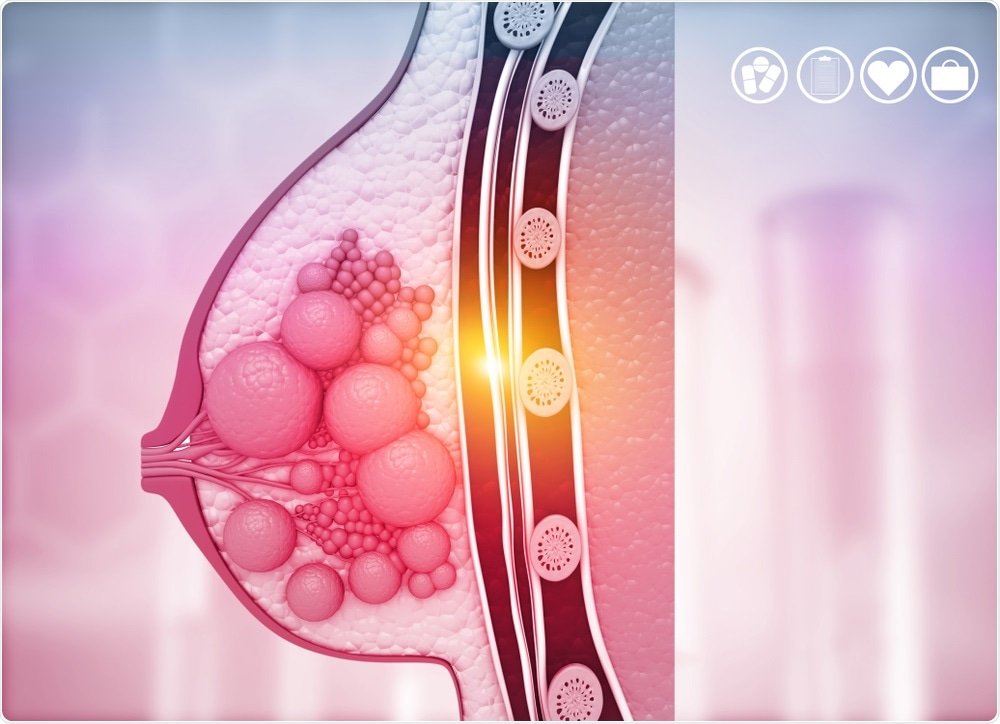
Breast cancer arises from abnormal cell growth in breast tissue, often fueled by genetic and environmental factors. Early detection and treatment, which can include surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and hormone therapy, are key to curing it.
Understanding the intricacies of breast cancer is essential for anyone concerned about their health. This form of cancer typically manifests within the cells of the breasts, potentially developing into a palpable lump or showing up on a mammogram before symptoms arise.
Known risk factors encompass a combination of lifestyle choices, genetic predispositions, and hormonal influences. With advancements in medical research, options for treating breast cancer have become more effective and diverse, allowing for personalized treatment plans that cater to individual cases. Emphasizing prevention through regular screenings and understanding one’s personal risk can significantly reduce the impact of breast cancer, making education and awareness as crucial as the treatments themselves.
Credit: www.news-medical.net
The Biology Behind Breast Cancer
Breast cancer stems from changes in breast cells. These changes can turn normal cells into cancerous ones. Understanding the biology of breast cancer is crucial. It helps us learn why it happens and how to tackle it. Here, we delve into the factors that lead to these critical changes and the role of genes and hormones in the cancer’s development.
Factors Leading To Cell Mutation
Certain elements can cause cells to mutate, leading to breast cancer. These factors include lifestyle choices, environmental exposures, and inherited traits. Cell mutation doesn’t always mean cancer, but it opens the door for potential disease. Here are some common factors:
- Smoking and alcohol use
- Radiation exposure
- Hormonal imbalances
- Aging process
Each factor can damage cell DNA. Damage doesn’t fix itself properly, which can lead to breast cancer.
Genes And Hormones In Breast Cancer Development
Genes carry the blueprints of our bodies. Some genes control cell growth. If these genes mutate, they can fail to regulate cell division. This uncontrolled growth can form tumors. Certain genes, like BRCA1 and BRCA2, are well-known for their links to breast cancer.
| Gene | Risk |
|---|---|
| BRCA1 | Higher risk for breast and ovarian cancer |
| BRCA2 | Increased susceptibility to various cancers |
Hormones also play a big part. Estrogen and progesterone can fuel the growth of hormone-sensitive breast cancer cells. This happens mainly during the reproductive years. Paying attention to family history and hormone levels is essential.

Credit: www.netmeds.com
Types Of Breast Cancer
Understanding the Types of Breast Cancer is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment. Breast cancer is not a single disease. It comes in several forms. Some grow slowly while others are aggressive. Knowing the type of breast cancer can help dictate the right treatment.
Invasive Vs. Non-invasive Breast Cancer
Invasive breast cancers spread beyond the milk ducts or lobules into nearby breast tissue. Non-invasive breast cancers stay inside their place of origin. They don’t spread. However, non-invasive can sometimes develop into invasive cancer.
- Invasive Ductal Carcinoma (IDC): This type starts in the milk ducts then invades nearby tissues.
- Invasive Lobular Carcinoma (ILC): It begins in the lobules and then spreads to nearby tissues.
- Ductal Carcinoma In Situ (DCIS): A non-invasive cancer contained within the milk ducts.
- Lobular Carcinoma In Situ (LCIS): It starts in the lobules but doesn’t invade other tissues.
Breast Cancer Subtypes And Their Significance
Breast cancer subtypes are identified through certain tests. These tests check for hormone receptors and HER2 protein on cancer cells. The subtype determines the treatment approach.
| Subtype | Significance |
|---|---|
| Hormone Receptor-positive | These cancers grow in response to hormones and can be treated with hormone therapy. |
| HER2-positive | Cancers with high levels of HER2 are treatable with drugs targeting this protein. |
| Triple-negative | Lacks receptors for estrogen, progesterone, and HER2. Chemotherapy is often used. |
| Triple-positive | These have receptors for estrogen, progesterone, and HER2. A combination of treatments is used. |
Recognizing Breast Cancer Symptoms
Recognizing breast cancer symptoms stands as a critical step in early detection. Symptoms are warning signs. They prompt individuals to seek medical advice. This could lead to timely interventions. Prompt treatment often improves outcomes.
Early Signs And Diagnosis
Early signs of breast cancer are important. They can look like simple changes. But these changes are not always cancer. They include:
- New lumps or thick areas in the breast or underarm
- Pain in any area of the breast
- Changes in breast size or shape
- Nipple discharge that is not milk
- Nipple changes, like pulling in
- Changes in breast skin, such as redness or dimpling
Diagnosis involves steps. It starts with a doctor visit. Then, a doctor will check for lumps. If found, they suggest tests. Tests include mammograms and biopsies. Insights from these help confirm cancer.
Advancements In Screening Techniques
Screening techniques are better now. They find cancer early. This leads to better treatment chances. Current advancements include:
| Technique | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| 3D Mammography | Creates a 3D picture of the breast | Spots abnormalities better |
| Ultrasound | Uses sound waves to make images | Helps examine dense breast tissue |
| MRI | Uses magnets and radio waves | Provides detailed pictures |
New technologies find cancer early. This is critical. It allows for swift action. It could mean less invasive treatment. It may mean a better chance of success.
Treatment Options For Breast Cancer
Understanding the best approach to treat breast cancer depends on many factors. Each case is unique. Plans often combine different treatments. They aim to remove cancer, reduce the risk of recurrence, and manage symptoms. Let’s explore modern treatment paths.
Surgery And Radiation
Surgery is a common first step. It attempts to remove cancer cells from the body. Two main surgery types exist: lumpectomy and mastectomy. A lumpectomy removes the tumor and a small rim of tissue. A mastectomy removes the whole breast.
Radiation therapy usually follows surgery. It uses high-energy rays. It targets remaining cancer cells. It often lasts several weeks. Radiation therapy limits the risk of cancer returning.
Chemotherapy And Hormone Therapy
Chemotherapy destroys cancer cells throughout the body. It involves medication cycles. These cycles run for a certain period. These drugs can help shrink tumors before surgery.
Hormone therapy is effective against hormone receptor-positive breast cancers. It blocks the body’s hormones that fuel cancer growth. Sometimes, hormone therapy lasts for several years post-surgery.
Emerging Targeted Treatments
Science has introduced new treatments targeting specific aspects of cancer cells. These targeted treatments are designed to avoid normal cells. They zero in on genetic changes in cancer cells.
- HER2 inhibitors: Target HER2-positive breast cancers.
- PARP inhibitors: Effective for women with BRCA mutations.
- Immune checkpoint inhibitors: Work by boosting the immune system.
| Type | Function |
|---|---|
| HER2 Inhibitors | Attack the HER2 protein on cancer cells. |
| PARP Inhibitors | Helps treat cancers with BRCA mutations. |
| Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors | Boost the immune system against cancer cells. |
Prevention And Early Intervention
Prevention and Early Intervention play crucial roles in the fight against breast cancer. Understanding the underlying causes helps pave the path for preventing its onset. While not all risk factors are within our control, adopting a healthier lifestyle can significantly reduce risks. Early detection blends hand-in-hand with prevention and can dramatically improve treatment outcomes.
Lifestyle Changes And Risk Reduction
Making positive lifestyle changes can reduce breast cancer risk. Here are key strategies:
- Maintain a healthy weight: Obesity increases risk, especially after menopause.
- Stay physically active: Routine exercise helps lower risk.
- Limit alcohol: Even small amounts raise risk.
- Eat nutritious food: A balanced diet supports overall health.
- Avoid smoking: It’s linked to a higher risk.
Some risks like family history, can’t change. Still, informing your doctor can help tailor your prevention plan.
The Importance Of Regular Check-ups
Regular medical check-ups lead to early breast cancer detection. Early diagnosis often results in better treatment success and survival rates. Here are the essentials:
- Monthly self-examinations: Familiarize with your breasts to notice changes.
- Annual clinical exams: A healthcare professional should check your breasts.
- Mammograms: Ensure you get routine mammograms as per health guidelines.
Discuss a personalized screening schedule with your doctor based on your risk factors. Remember that early action can save lives.
Survivorship And Quality Of Life
Embarking on a journey through breast cancer treatment can be daunting. Post-treatment, the focus shifts towards thriving as a survivor and enhancing life quality. It is here that understanding and cultivating robust support networks and effective long-term health management strategies can lead to a fulfilling life, post-recovery.
Support Systems For Recovery
Strong support systems are vital for recovery. They provide comfort, aid, and encouragement. Friends, family, and survivor groups contribute to emotional and practical support networks.
- Counseling – Professional guidance helps in coping with emotional upheaval.
- Survivor Networks – Connection with fellow survivors can be empowering.
- Community Programs – Access resources, workshops, and events geared towards survivorship.
Tailored support programs also address specific needs, including physical rehabilitation and dietary advice. These programs are essential for regaining strength and returning to daily activities.
Long-term Health Management After Treatment
Following treatment, maintaining health is crucial. A balanced lifestyle with regular medical check-ups is key to this phase.
| Health Aspect | Actions to Take |
|---|---|
| Physical Activity | Engage in daily exercise to boost energy and mood. |
| Nutrition | Eat a balanced diet rich in nutrients to rebuild the body. |
| Mental Wellness | Practice stress-relief techniques such as meditation or yoga. |
| Follow-Up Care | Attend regular screenings and check-ups with healthcare providers. |
Incorporating a mix of self-care practices, ongoing cancer surveillance, and preventive measures is essential. This helps mitigate the chances of recurrence and sustains overall well-being.
Remember, the journey does not end at treatment. Both physical and emotional recovery take time, care, and attention. Embrace each step towards a life defined not by cancer, but by courage, health, and strong support.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/breast-cancer-staging-5207190-FINAL-941ccd55a0774caaa2c181a816119e9a.jpg)
Credit: www.verywellhealth.com
Frequently Asked Questions For Why Breast Cancer Occurs And How To Cure It
What Causes Breast Cancer In Women?
Breast cancer in women can result from genetic mutations, hormonal changes, and environmental factors. Lifestyle choices such as diet or alcohol consumption, and family history of cancer, particularly BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene mutations, are significant contributors.
Can Breast Cancer Be Completely Cured?
Breast cancer can be cured, especially when diagnosed early. Treatments like surgery, chemotherapy, radiation, and hormone therapy have high success rates. Long-term remission and survival depend on the cancer stage and individual response to treatment.
How To Detect Breast Cancer Early?
Early detection of breast cancer involves regular self-examinations, mammograms, and clinical breast exams. Awareness of changes in the breast, such as lumps, skin dimpling, or nipple discharge, is crucial for early detection and treatment.
What Are Breast Cancer Treatment Options?
Treatment options for breast cancer include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, hormone therapy, and targeted therapy. The choice depends on the cancer stage, type, and patient’s overall health. Personalized treatment plans are crucial for effective results.
Conclusion
Understanding the intricacies of breast cancer is crucial. Early detection and modern treatments offer hope. Lifestyle changes can also play a part in prevention. Still, ongoing research is critical to unearth further cures. Let’s keep advocating for awareness and supporting those affected.
Together, we fight stronger.